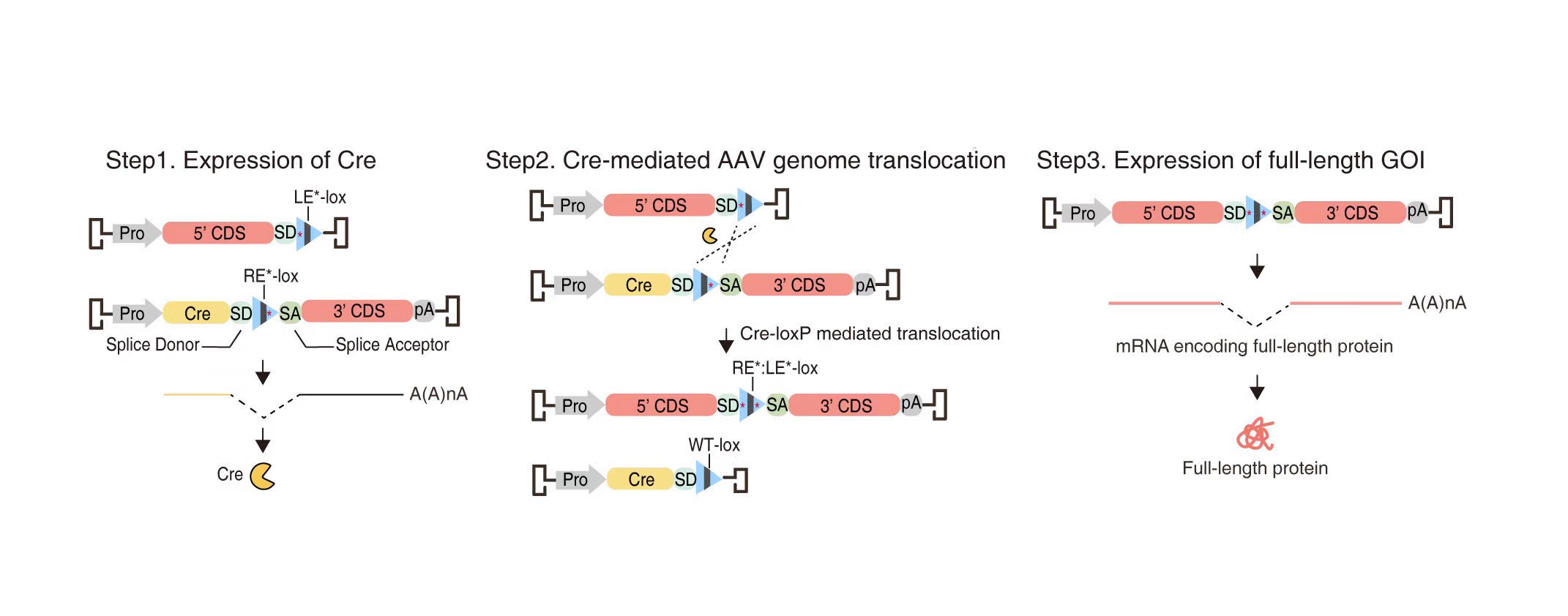

AAVLINK is a DNA recombination-based method for large gene delivery using adeno-associated virus (AAV), a leading vector in gene therapy. Genes exceeding packaging limit of AAV are split into two or three fragments and are reconstituted through the following steps:
Pro: Promoter; LE*-lox: Left element mutant lox sites; RE*-lox: Right element mutant lox sites; Cre: Cre recombinase; SD: Splice donor; SA: Splice acceptor; pA: Polyadenylation signal.
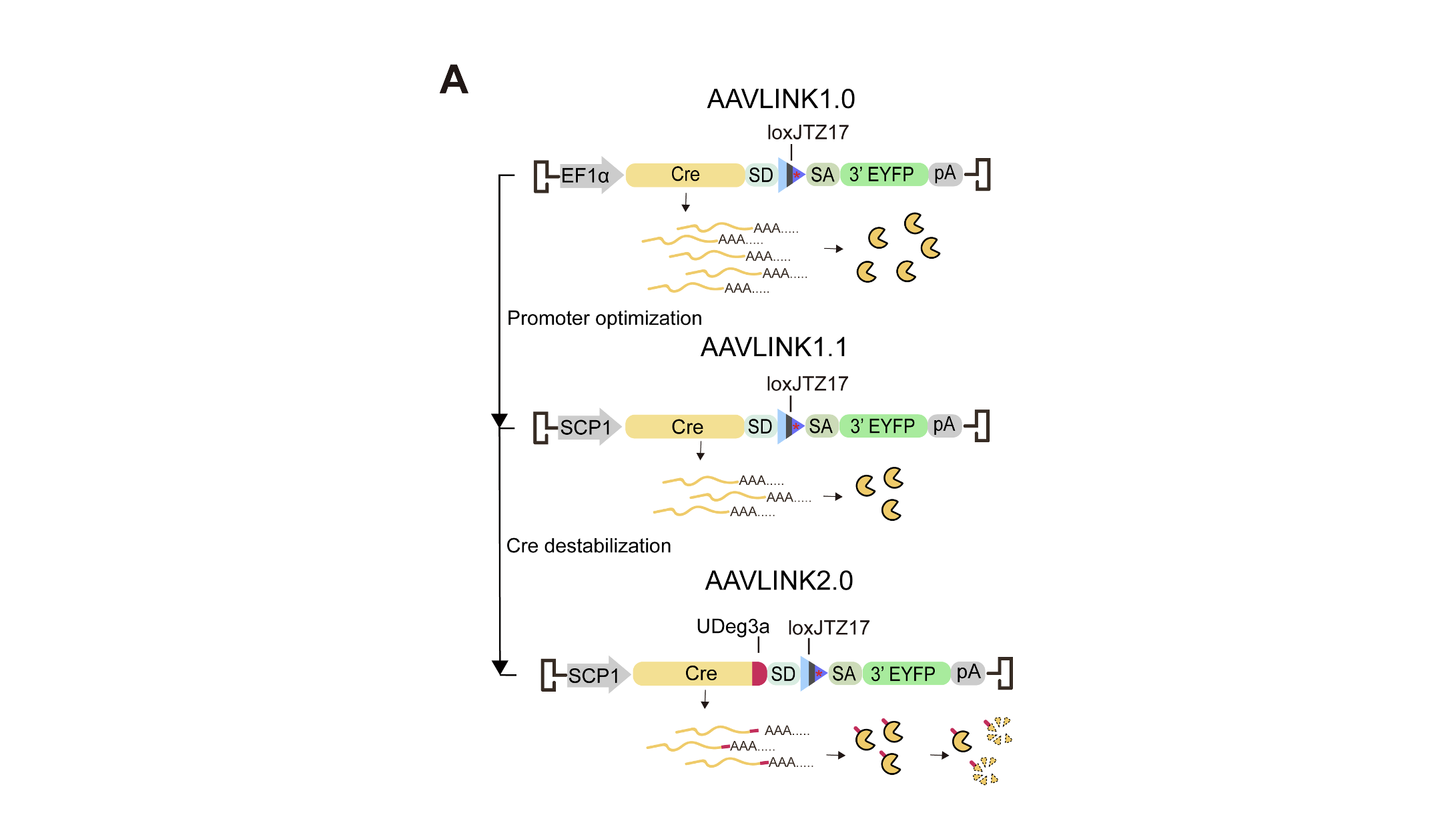
AAVLINK2.0 enables minimization of Cre expression, without compromising gene cargo reconstitution.
Key improvements in AAVLINK2.0 include:
SCP1: Weak synthetic promoter; UDeg3a: Protein degradation tag; Cre: Cre recombinase with degradation tag; Other elements: Maintained from AAVLINK1.0 system (LE*-lox, RE*-lox, SD, SA, pA).
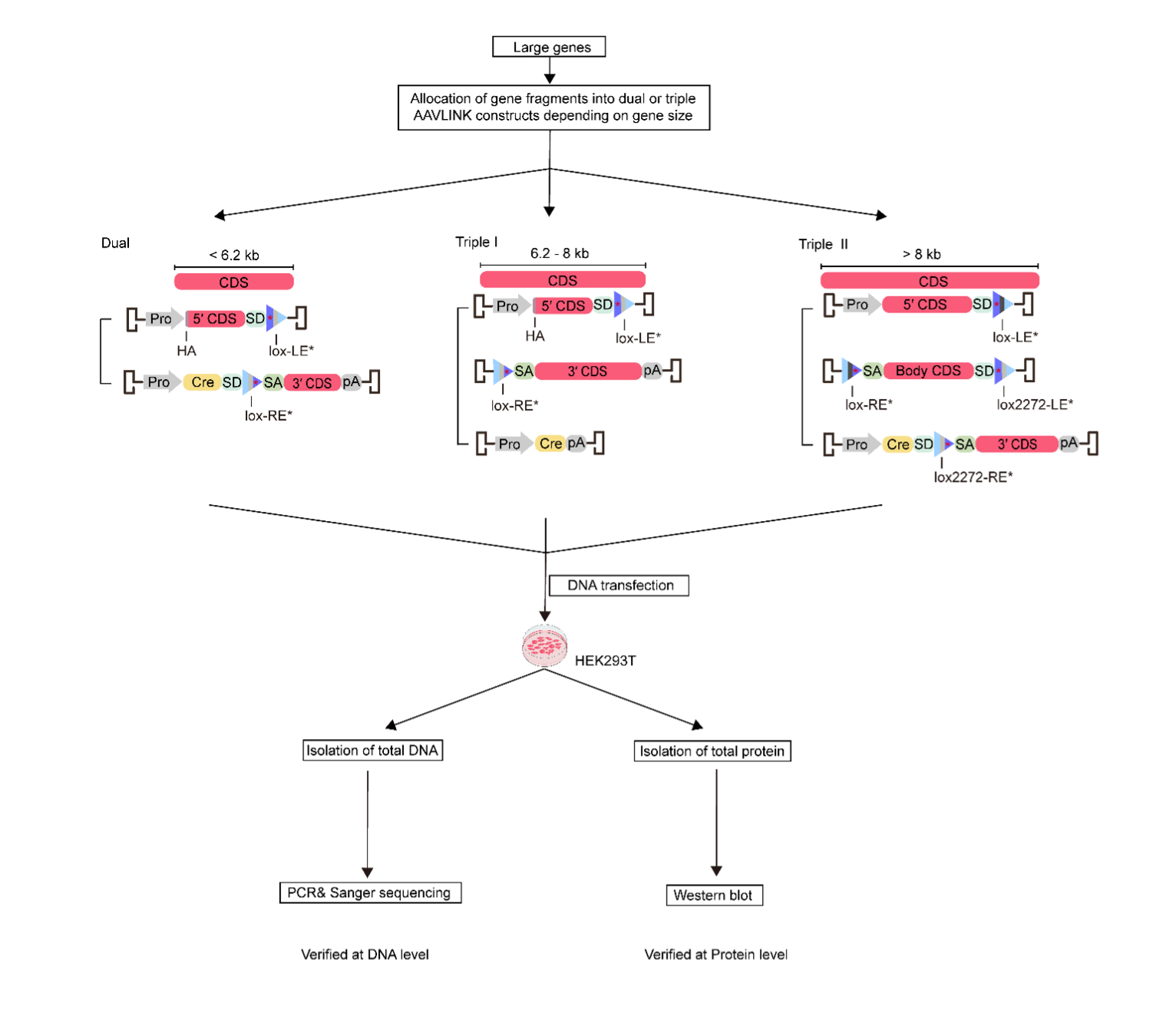
A total of 198 genes (193 disease-relevant genes and 5 CRISPR genes) were allocated to bipartite or tripartite AAVLINK vectors depending on their sizes.
The reconstitution of full-length genes was verified at DNA or protein levels, following transfection of HEK293T cells with these constructs.
Key steps in the process include:
Pro: promoter; Cre: Cre recombinase; SD: splice donor; SA: splice acceptor; pA: polyadenylation signal; lox-LE*: left element mutant lox sites (the JT15 or JT1571 sites were used in the resource, JT1571 is a variant of JT15); lox-RE*: right element mutant lox sites (the JTZ17 site was used in the resource); lox-LE:RE: left element and right element mutant lox sites.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) risk genes as listed in the SFARI Gene database.
Non-ASD genes: genes with loss-of-function mutations that cause disease.
CRISPR Tools: a series of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing tools.
Learn more about our team and contact us.